Limehouse and East India: I spent most of Saturday 11th June 1994 wandering in the area between Limehouse, Blackwall and the former East India Docks, concentrating on making panoramas, some of which were the post Limehouse, Poplar, Blackwall and East India Panoramas – 1994 but I also took a number of black and white and colour images. You can find more of both in two Flickr albums – links at the bottom of this post – but here is some of the colour work. These pictures will have been made using an Olympus OM$ camera on Fuji film. I carried a range of lenses from 21mm to 200mm, though probably most all were taken with 28mm or 50mm lenses.
The eastern entrance to the Limehouse Link Tunnel which was officially opened in 1993. Both portals have decorative sculptures, this one an untitled abstract by Nigel Hall which I find it hard to find any point in. The 1.1 mile tunnel took 4 years to build and cost £293,000,000 making it the most expensive road scheme in Britain per mile.
This is the Limehouse Link Eastern Service Building. With a huge volume of traffic passing through the tunnel presumably the main service needed is ventilation and those chimneys presumably are on top of huge fans for the purpose, sharing the pollution with the community.
The story of Dunbar Wharf is told on the Isle of Dogs Life web site in the article Dunbar Wharf and the Remarkable Story of Duncan Dunbar, and I’ve written more about it in previous posts. Duncan Dunbar made a fortune as a brewer and wine merchant and on his death in 1825 his son, also Duncan Dunbar used this to set up a large shipping fleet, becoming one of the richest men in Britain.
As well as goods to and from the world Dunbar’s shipping line made 37 trips carrying convicts to Australia and were troopships for the Crimean War. He never married and had no children and on his death in 1862 the ships were all sold and the business closed.
The buildings here date from the mid 19th century and are Grade II listed.
I think this was the window of a tailor’s shop in Limehouse, but cannot recall its exact location. The caption I gave it came from the black and white poster at the back which I suspect is from the 1920s or 30s, though I’m certainly no fashion expert, while the blue framed image at lower left looks to me a little older and has an interesting lady golfer.
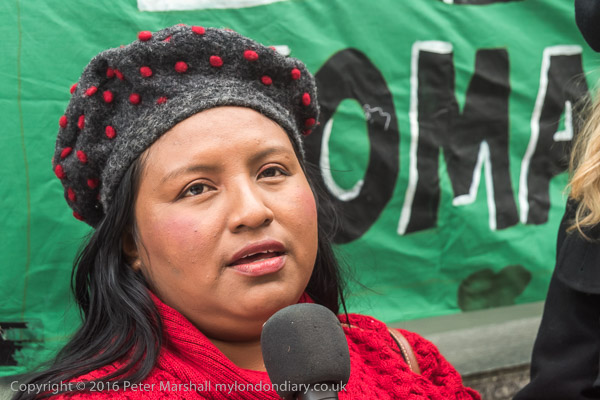
Limehouse and Poplar used to be London’s Chinatown before that moved to Soho, and some traces remain, rather more back in 1994 than now. On the wall is a calendar for the ‘Year of the Dog’ and a notice informing us that:
‘*WE NOW SELL
‘CHICKEN’ BALLS’ IN BATTER
PLEASE ASK STAFF
£2 A PORTION THANK YOU’
The two green hexagons floating in the centre close to the top of the picture (with some more very faint and above them to their right) are photographic artifacts, lens flare, images of the lens iris reflected from some interior lens surface from a light source just outside the frame. But I rather like the effect here.
Looking through a window into a hairdressers with a red-edged counter and mirrors, red chairs and red towels hanging on hooks seen in the mirror. It wasn’t possible for me to get enough depth of field to make everything in the picture pin sharp, but this perhaps makes the mirrored image stand out a little more.
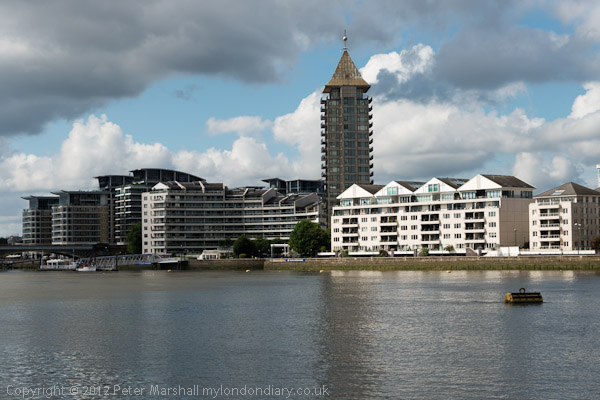
The lane closer to the centre of the image dives here into the East India Dock Tunnel with the red brickwork of the tunnel mouth at the right of the picture. The tunnel was opened in 1993. At the left is Canary Wharf Tower, then in isolation, in front of it the bridge and red tower of East India DLR station. The rather depressing 1990 ten-storey granite clad post-modern office blocks on the site of the main East India Dock have now been comprehensively redeveloped mainly for residential use and rebranded as ‘Republic’.
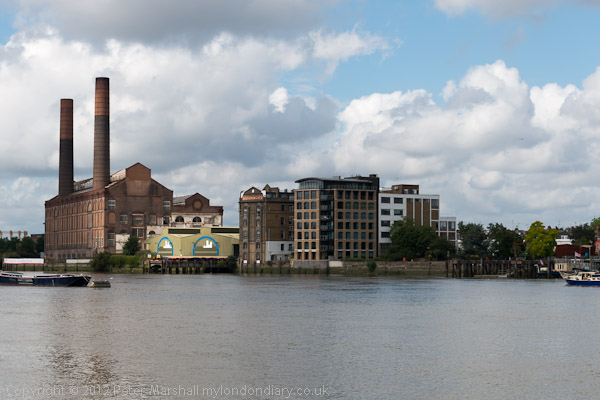
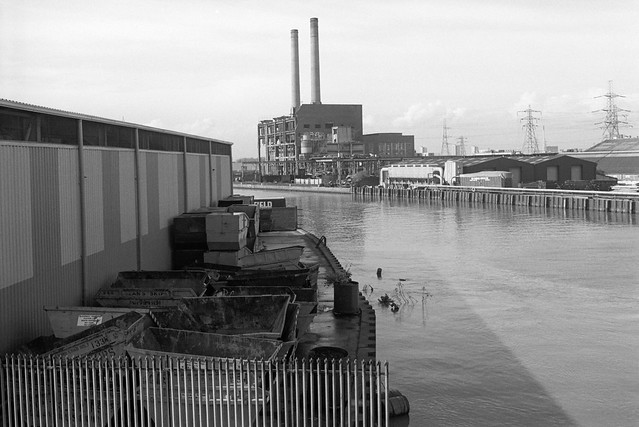
Further east also looking back to Canary Wharf from underneath the DLR viaduct with the former switchgear house of Brunswick Wharf Power Station at right. Planned in 1939 but not built until after the war this was a coal fired power station on the site of the East India Export Dock. In 1948 the dock was filled in but post-war financial constraints meant the power station was only became operational in 1952, and finally completed in 1956.
In 1970 it was converted to burn oil, probably to reduce air pollution in London. Increases in oil prices later made this one of the more expensive generating stations and it was closed in 1984 and sold for redevelopment in 1987.
Most of the power station was demolished in 1989 but this building remained, I think until around 2005 when it was demolished for a large residential development, Virginia Quays, which has on the riverbank the 1951 Grade II listed Virginia Quay Settlers Monument.
My 1984 albums on Flickr:
1994 London Colour
1994 London Photos (Black and White)
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.