Any remaining doubts about the Tory party’s intentions to privatise the NHS should have been eliminated by the recent appointment of Samantha Jones, the outgoing chief executive of Operose Health, as an “expert adviser for NHS transformation and social care“.

Openrose is the British subsidiary of giant US private healthcare firm Centene, and recently bought AT Medics, a GP led company that was ran many of London’s GP surgeries and other primary care services. Openrose was already running around 20 GP surgeries as well as various opthalmology services, a dermatology clinic in Kent and an urgent treatment centre in Birmingham.

Despite health secretary Matt Hancock’s claims that his proposed changes to the NHS would put an end to 30 years of NHS privatisation, the process is currently being accelerated, with these and other changes making it easier for US and other companies to take control of parts of the NHS.
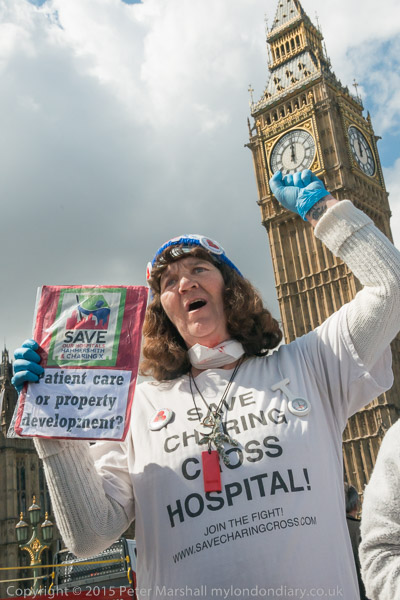

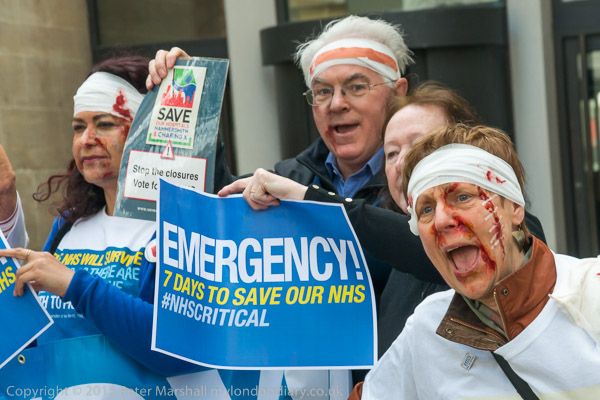
The launch of the ‘7 Days to Save our NHS’ Campaign’ on April 30th, 2015 came a week before the 2015 General Election, and urged people to use their vote on May 7th to save the NHS. It was one of many protests against the creeping privatisation of our health service that I’ve photographed, along with more protests over hospital closures and other attacks on the service which left it in a poor state at the start of the Covid pandemic.

Fortunately – and largely thanks to the dedicated work of NHS staff – it more or less coped, but at the price of far too many deaths in hospitals and care homes, with high levels of hospital-acquired infection due to a lack of proper protection – and we saw photographs of staff having to improvise with bin bags.

But although some of us could have used our vote to try to save the NHS, for many their was no such credible alternative. Both of our major parties have been guilty of privatising the NHS, with New Labour responsible for much of the present crisis in our healthcare system, particularly for saddling hospital trusts with crippling long-term debts through insanely thought out and poorly negotiated private finance initiative hospital building projects – which have forced programmes of hospital closures. The https://www.express.co.uk/news/uk/355999/Who-now-owns-the-NHS-and-can-they-cure-it Daily Express described these in 2012 as “a Klondike gold strike for investment firms” which will result in the taxpayer paying £301billion to receive facilities worth £57.4 billion.
And many MPs – mainly but not entirely Tory – are very much in on the gravy train that NHS privatisation is already providing, and very much rubbing their hands in anticipation of more. In 2015 the https://www.mirror.co.uk/news/politics/former-private-health-firm-chief-23838725 Daily Mirror published what they called a full list of MPs with links to private healthcare firms. Among the 70 on that list were the then prime minister David Cameron, Andrew Lansley, described as ‘Former Health Secretary & architect of privatisation’, former Home Secretary David Davis, and most of the leading Tories – including current secretary of state for health and social care Matt Hancock MP.
NHS banner on Westminster Bridge
‘7 Days to Save our NHS’ Campaign launch
All photographs on this and my other sites, unless otherwise stated, are taken by and copyright of Peter Marshall, and are available for reproduction or can be bought as prints.