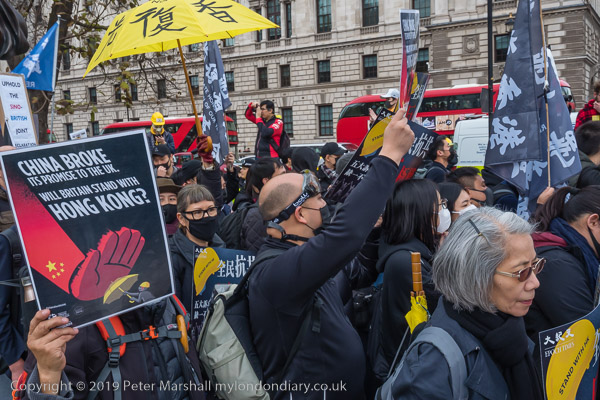
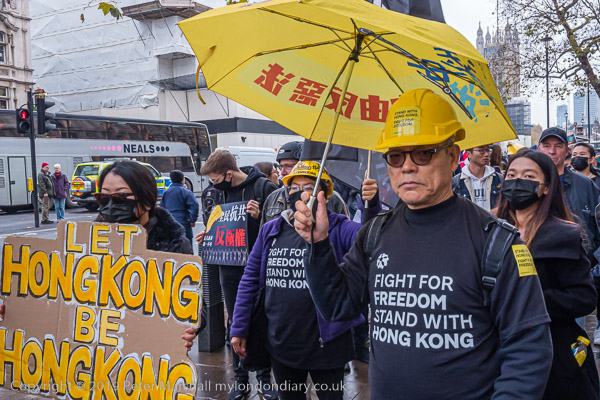
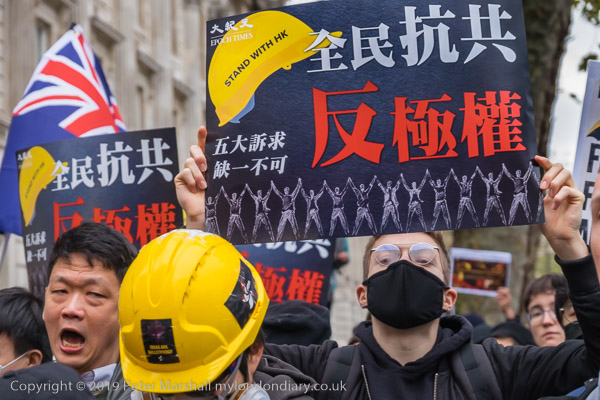
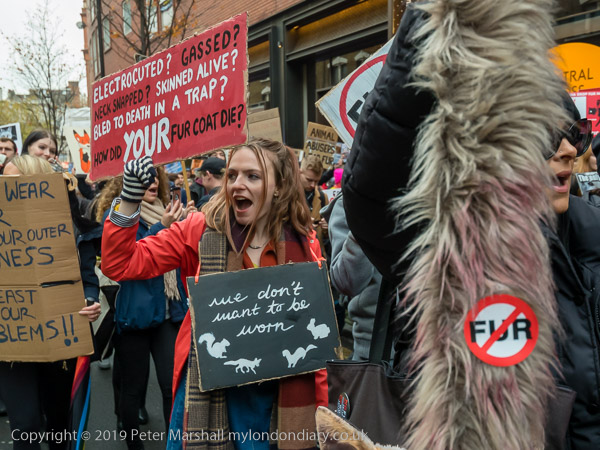
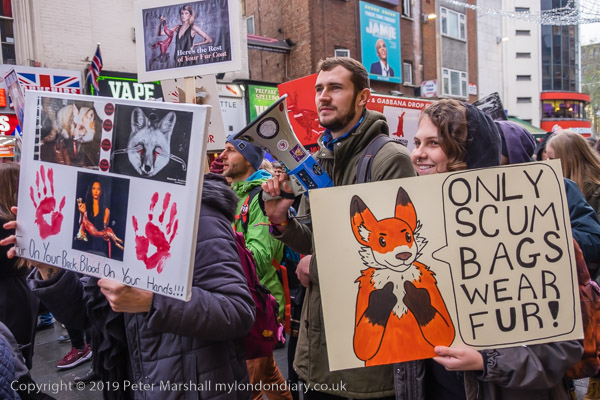
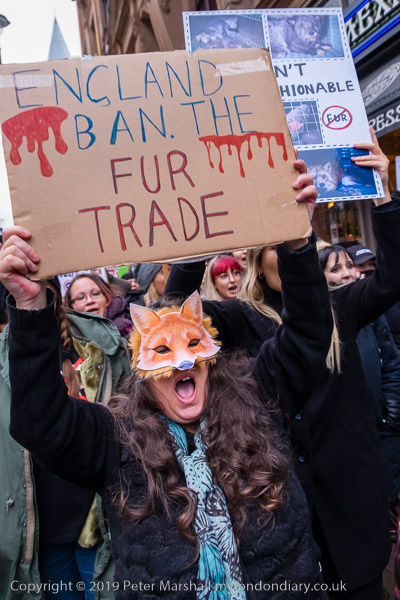
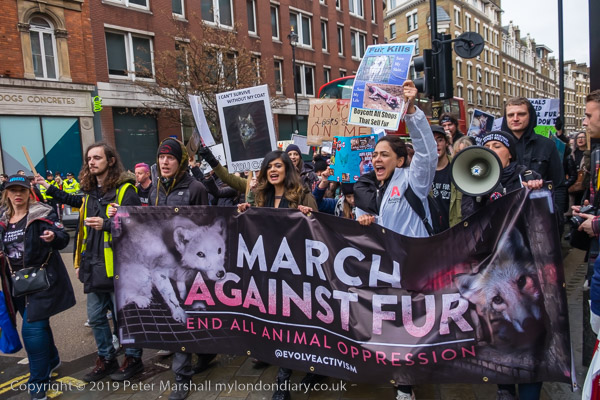
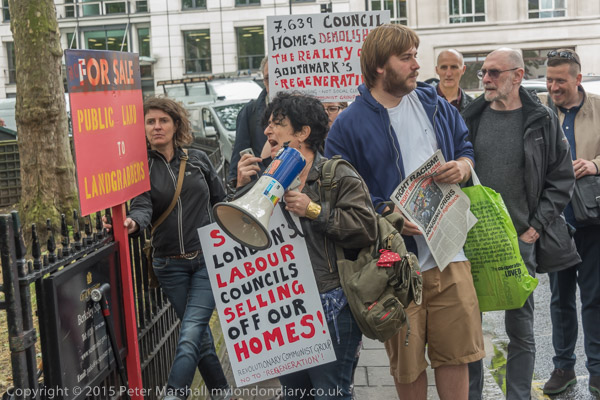
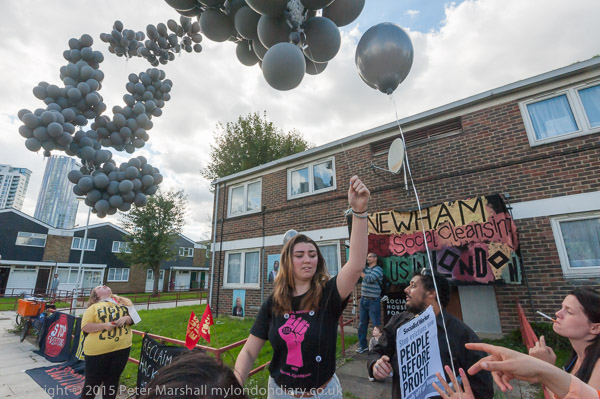Gate Gourmet & a Bike Ride: On Sunday December 4th 2005 I got on my bike and rode the roughly 1l miles to Southall, where I locked up my bike (not the Brompton, but an old CinellI racer I’d got many years ago for my 13th birthday) and photographed a protest by workers sacked from their jobs at Heathrow airport catering firm Gate Gourmet.
There is an excellent article on the Striking Women website which gives the background to the dispute and explains why 56 women workers of South Asian origin felt betrayed by the agreement reached by the TGWU over the dispute and refused the compensation offered of between £5000 and £8000 – and refused to leave quietly – though most of the workers took the money rather than fight for justice.

The workers and their shop stewards received little support from the official trade union movement in their fight for justice and the TGWU hardship fund ended its support in January 2006, and the TGWU (by then part of UNITE) cease all support in 2009. Around a dozen of the workers – mainly those who were for various reasons not at work when Gate Gourmet locked the workers out – eventually won claims for unfair dismissal.

The dispute made very clear the extent to which union powers had been emasculated by a succession of Acts passed under Thatcher – the Employment Act 1980, Employment Act 1982, Trade Union Act 1984, Trade Union Art 1990, Employment Act 1988, Employment Act 1990. John Major continued with the Trade Union Reform and Employment Rights Act 1993 and then Blair and New Labour took over the job.

But even given all this, the TGWU ended up caving in to the employers and giving them everything they wanted in the settlement it made.
Below (with minor corrections) is the post I wrote back in 2005.
Gate Gourmet – the Struggle Continues
Southall, December 4, 2005

Gate Gourmet was split off from British Airways in 1997 to cut costs by out-sourcing their catering. It was sold to US company Texas Pacific in 2002, and they also decided to cut costs. This seems to have meant increasing workload, bringing in more managers (why?) and replacing skilled and experienced staff by unskilled workers. They went into a dispute with the TGWU (Heathrow’s major union) over layoffs and worsening conditions, then on 10 August 2005, took on 120 temporary workers.
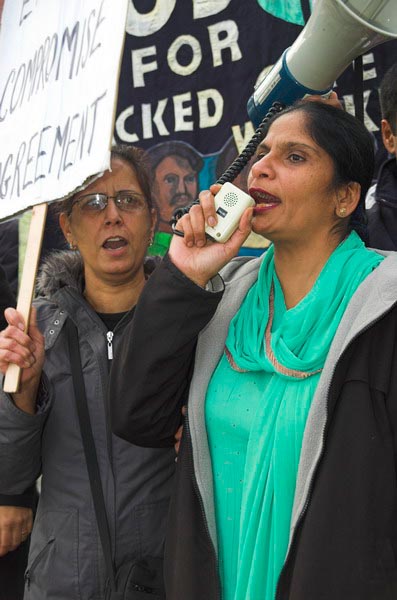
Their aim was to provoke an unofficial walkout, which would allow them to sack the workers. The workers held a union meeting in the canteen and were told by management that if they were not back at work in 3 minutes they were all sacked. It is claimed that management had locked the doors just to make sure they didn’t return. The workers were then forcibly evicted from the premises by the private security guards the management just happened to have standing around waiting.

Britain’s anti-union laws (thanks to Mrs Thatcher) stack the odds against workers, allowing unscrupulous management to get away with most things short of murder if they put their minds to it.

The TGWU were hamstrung by a High Court injunction, which prevented them from doing much to help the workers. The only thing that helped them was illegal action by their former colleagues at BA, said to have cost that company £40 million. So eventually BA forced Gate Gourmet to come to some kind of compromise with the TGWU, but this has failed to satisfy most of the workers, who wanted their jobs back and decent working conditions. So, although all the papers reported it as over, the action still continues. When my wife flew BA from Heathrow a few days ago, she got a voucher to get sandwiches in the departure lounge rather than in-flight catering.

This is a dispute that highlights the need for proper trade union laws that give workers and unions a fair deal. It shows how union weakness has allowed the Labour Party to renege on the promises it made in opposition and to turn its back on its traditions of fair play. BA has also emerged as pretty short-sighted in its decision to out-source its catering, much as we have found out-sourcing to be a mistake over key services in hospitals and schools.
More pictures on My London Diary
Around Heathrow
December 4, 2005

After the protest I was relieved to find my bike still in one piece where I had locked it and rode home. On my way to Southall I had time to spare and stopped to take a few pictures -and just a few more on my way home. Here is what I wrote in 2005.
I took my usual route to Southall on a push-bike – it takes me around 45 minutes if I don’t stop. but I nearly always do stop at least once to take some pictures. So here are a few pictures from around Heathrow, including a farm. Heathrow swallowed up some of the most productive arable land in the country including a number of fine orchards, but there are still a few farmed areas around its edges – cutting down the dangers of a crash, although some of the most used approaches come in low over many homes.

It was never a suitable site for a major airport, but the chances of any government biting the bullet and closing it down seem low. We should have been running it down for years, but instead have built 2 new terminals (both of which the airport authority said they would never need) and further disastrous development looks likely.
A few more pictures on My London Diary.
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.