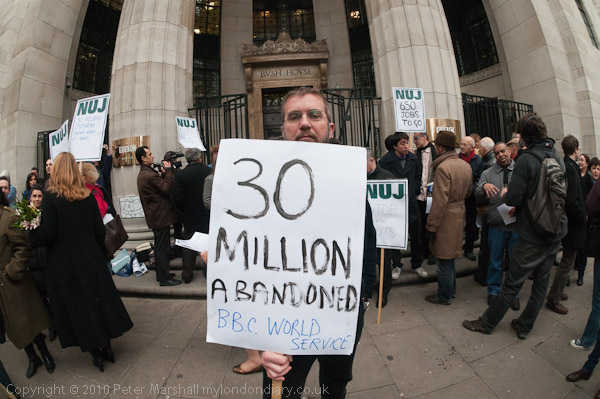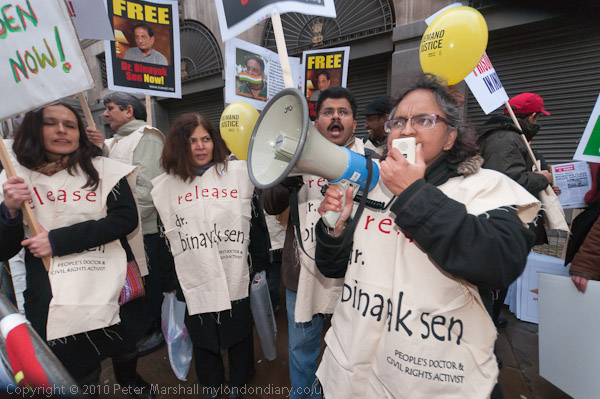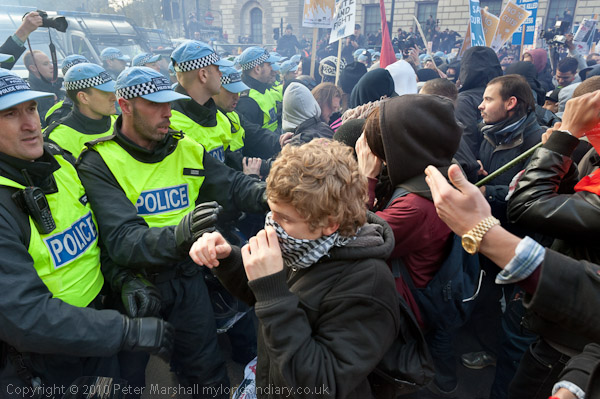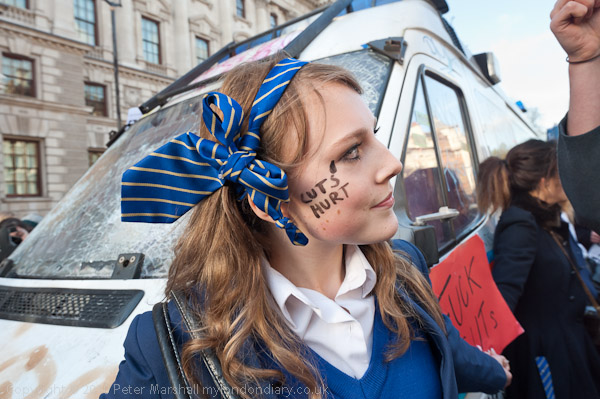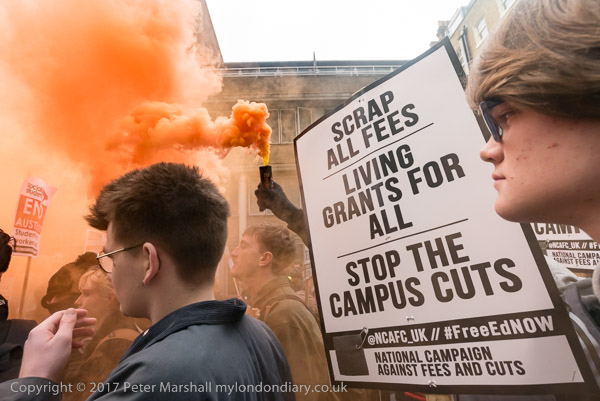Six days earlier a march against the Browne Review of Higher Education Funding, which had advocated an increase in tuition fees, allowing them to rise to £9000 a year, as well as the scrapping of the Educational Maintenance Allowances (EMA) for 16-18 year old and other changes including closing many arts and humanities courses had led to an angry confrontation between students and police when police decided to halt and kettle the march in Whitehall.

I had been there and reported at some length on the events, including the smashing of a worn-out police van which seemed to have been deliberately left by the police “as a plaything for the protesters” and charges in which some “police made pretty liberal use of their batons and a couple clearly went a little berserk“, and protesters were in danger of being crushed, screaming that they couldn’t breathe.

It hadn’t been like those protests I had taken part in during the late 60’s and most of those taking part “were probably well-behaved students on their first demonstration” who when more militant students breached the police lines “just stood around wondering what to do rather than following them.”
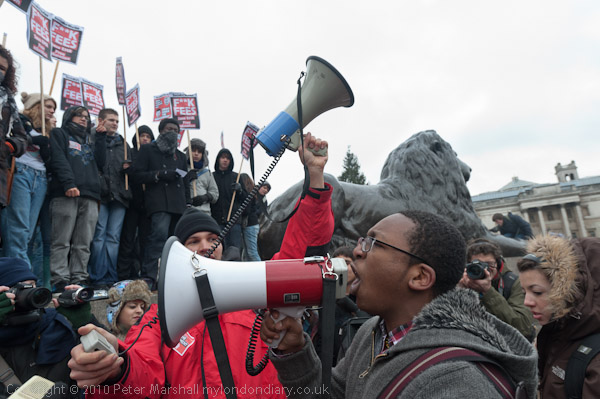
I concluded:
“It had been a pretty confused situation, and it seemed to me that neither police nor students came out of it with much credit. The police tactics seemed designed to create public disorder by kettling and a small minority of the students rose to the bait. Although most of the students were out for a peaceful march and rally and to exercise their democratic right to protest, the police seemed to have little interest in upholding that right.”

The following Tuesday around 5000 students came back to Trafalgar Square for what was meant to be a peaceful march at 1pm along the same route down Whitehall to a rally in Parliament Square – which had been agreed in advance with police. I think both sides wanted to avoid a replay of the previous week.

But shortly after noon, more radical students, including a group of younger students who would lose the EMA took to the plinth under Nelson’s column and called for the crowd to go down Whitehall and demonstrate at Downing Street; several hundreds followed them.

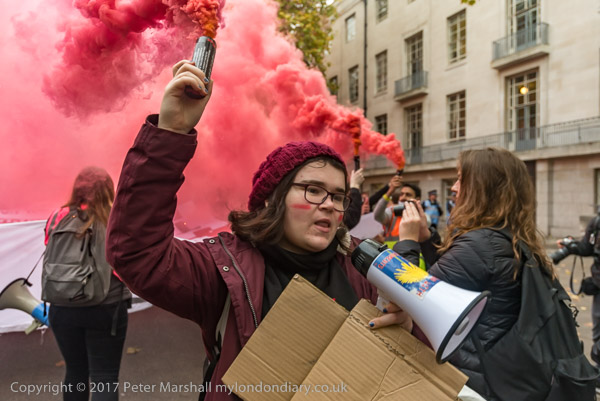
There were only a few police at the top of Whitehall and clearly they stood no change of stopping them, but their attempts to do so heightened the tension and when police formed a tighter line further down Whitehall the protesters began shouting that they were being kettled.

They turned around and went under Admiralty Arch and on to the Mall before continuing down Horse Guards Road. Police followed them, walking beside them as they crossed into Storey’s Gate, then turned into Parliament Square.

By now this group of protesters – perhaps by then a thousand or two were obsessed with the idea that they were being kettled – and certainly there were a large number of police in Parliament Square, particularly behind barriers set up in front of Parliament and at some of the exits from the square.

The protesters turned around and walked and ran, beginning a “long rather rapid walk around London“, rather painful for me as I was still suffering from a foot injury, “taking in Hyde Park Corner, Piccadilly Circus, Oxford Circus and Oxford Street and turning down Kingsway at Holborn and then walking into the City of London along Fleet St” with a couple of hundred police walking along the side of the march.

Most of the Met police stopped at the City of London boundary as the march continued “past St Pauls, the Stock Exchange, on up some of the narrow winding streets around St Bartholomews Hospital (it rather looked as if they were trying to kettle themselves there) to Smithfield Market before going back along Holborn Viaduct where I eventually left them to catch a bus and make my way back to see what was happening in Trafalgar Square.” The City of London Police had seemed to ignore the march and there was little or no trouble on their patch.

In Trafalgar Square there were still some of the original demonstrators but things were pretty quiet. There were police at the exits but people could walk past in both directions; “the protest was being isolated and watched rather than being kettled.”

Some of those I had been marching around London with made their way back into the square and there were a few short speeches before one of the official organisers announced that the demonstration was over and police would be happy for people to leave in small groups towards Charing Cross Station.

But most people decided to stay on and there were a few scuffles with police, with other students “linking arms in front of the police to protect them and stop any violence.”

It was snowing and beginning to get dark and it seemed to me that little further was happening so I walked out of the square and went home. It had been a confusing and tiring day for me. Later I heard that small group who had remained in Trafalgar Square had been kettled and some had been arrested.
More at Students Fees Protest – Day 2.
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.