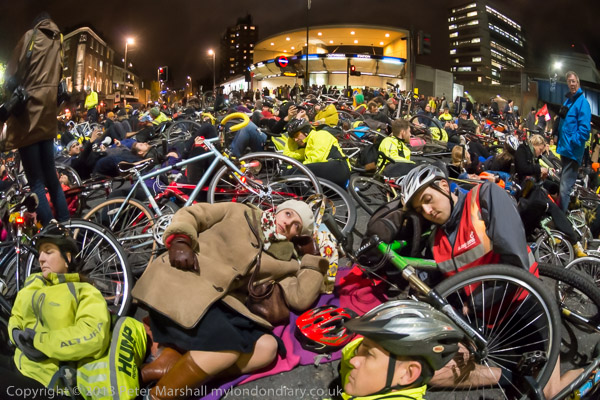
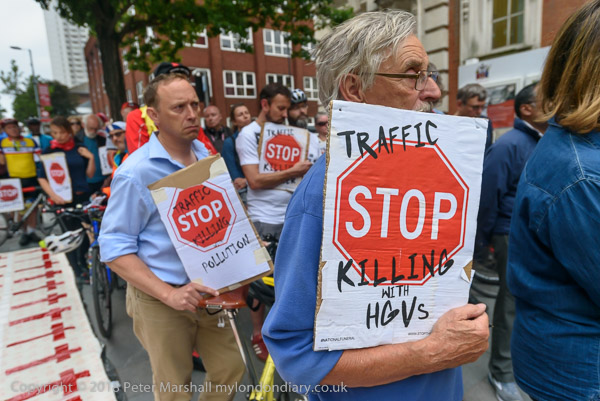
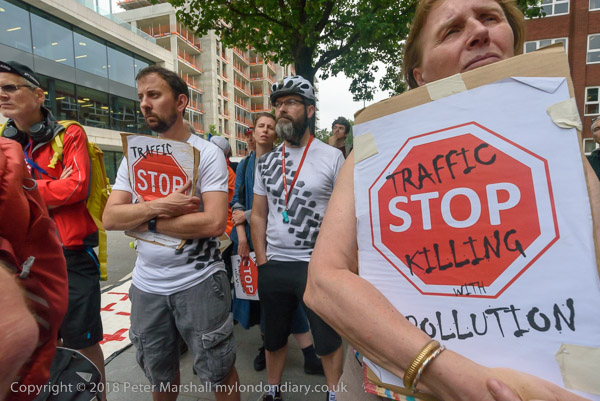
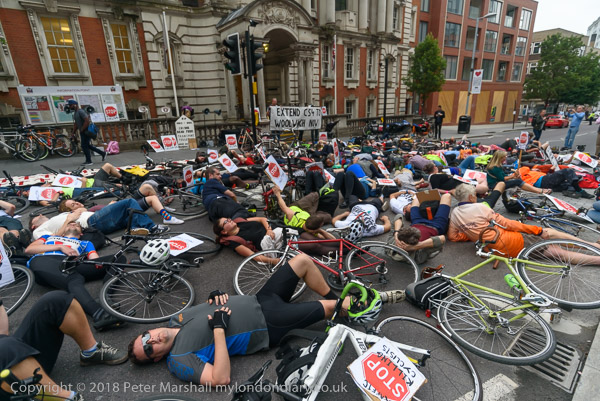
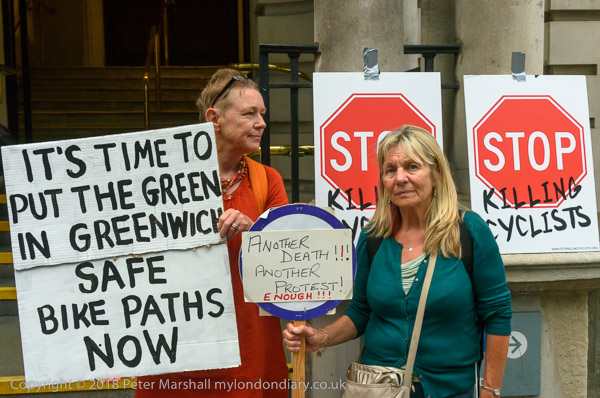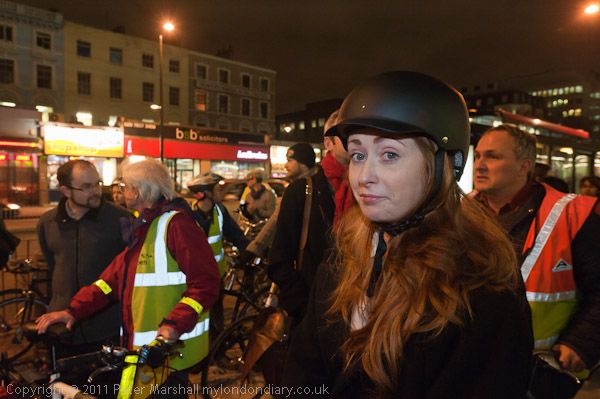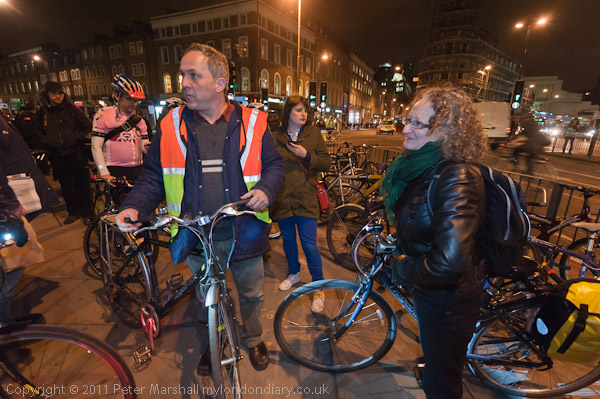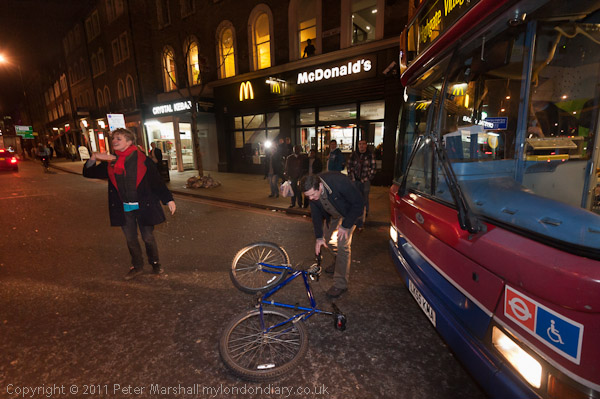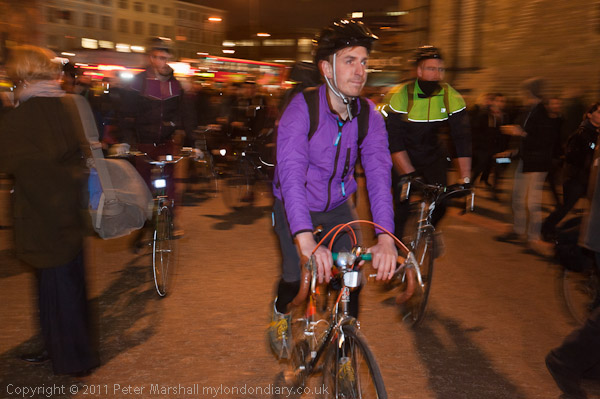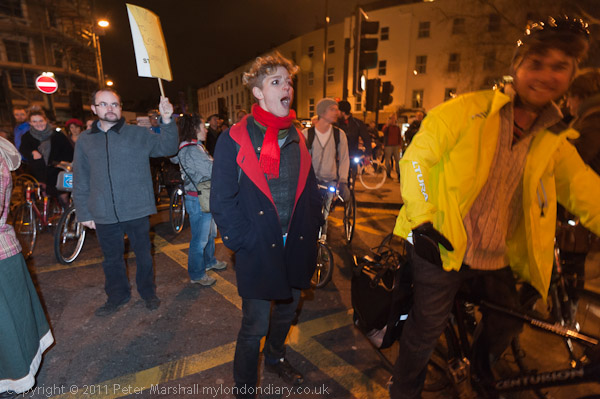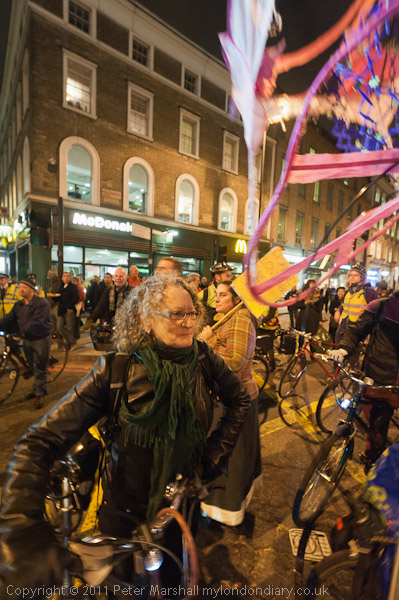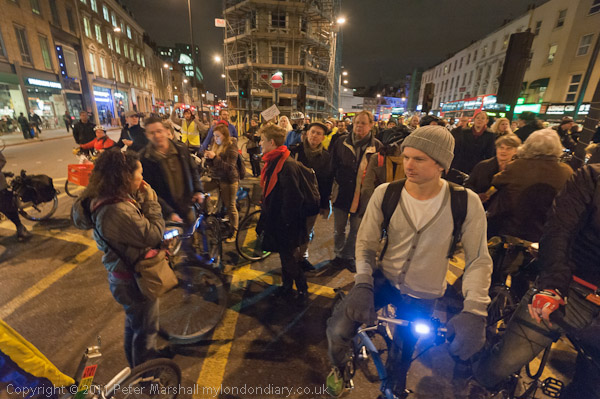Intellectual Property, Naked Cyclists: On Saturday 9th June 2012 after a rally against the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement outside Europe House in Smith Square I went to Hyde Park Corner where cyclists were preparing for the London World Naked Bike Ride, an environmental protest against a society based on oil and the domination by cars.
Rally Against ACTA

Current debates on intellectual property in 2025 are mainly concerned with protecting the rights of individual creators from being used without permission or compensation by companies developing AI which could then use the data taken to create new works which would mimic their work, essentially producing counterfeit works.

Back in 2012 the protests were against ACTA, the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement put together in secret talks between the USA, Europe, Japan and some other major governments to protect the copyrights, trademarks and patents held by major multinational companies.

Wikileaks had released the secrets of these talks, deliberately set up in private to exclude the views of civil society and developing countries. They proposed putting draconian powers in the hands of major corporations without the need for allegations of abuse to be properly tested.
Now in 2025 the government is attempting to put into law an act which would legitimise the production of ‘fakes’ by the major AI companies, though the fight against this is being carried on largely in the House of Lords rather than on the streets or on the web. As usual laws are largely about protecting and advancing the interests of the rich and powerful – whose donations and lobbying keep our legislators on side.

As well as preventing much sharing of material on the web – some legitimately – ACTA would also disrupt much-needed generic medicines to majority world countries, where indiscriminate raids had already disrupted some legitimate supplies. And many musicians and other content creators feared it would be used by the major corporations to prevent or inhibit their ability to profit through distributing their own work via the Internet.

On 4th July 2012, 478 MEPs in the European Parliament voted against ACTA, 39 in favour, and 165 abstained, meaning the agreement did not enter into force in the EU.
More about the protest and about ACTA, along with more pictures on My London Diary at Rally Against ACTA.
Naked Cyclists Ride Against Oil

Around a thousand cyclists in various states of undress, some wearing nothing but shoes, took part in the World Naked Bike Ride, an annual environmental protest touring central London, much to the astonishment of many tourists. Shoes are required, but otherwise the dress code is “as bare as you dare.”

Public nudity is not illegal in Britain and the ride seems to cause a great deal of hilarity from some onlookers but little or no offence. Most of those on the pavements were tourists and eagerly taking photographs of the event.
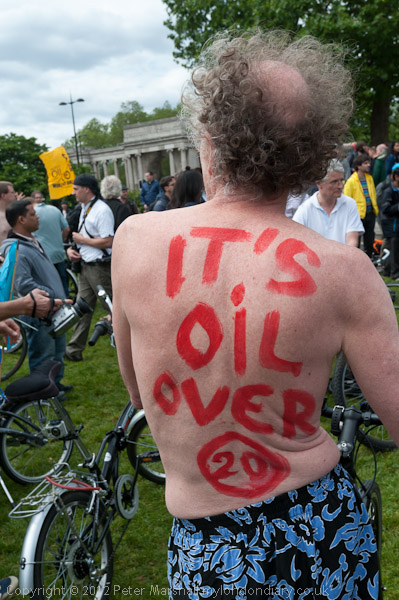
Although there had been many earlier naked bike rides organised as naturist or political demonstrations, the first World Naked Bike Rides were organised in 2004 and now take place in many cities around the world. The rides are a protest against dependence on oil and other forms of non-renewable energy and “expose the unique dangers faced by cyclists and pedestrians” in modern cities.

In 2012 there did seem to be a rather clearer environmental message than in some other years, and my pictures here – and in the many more on My London Diary concentrate on this rather than the nudity, and on the many with body paint, sometimes solely for decoration but often expressing an environmental message, contributing to the purpose of the ride to “deliver a vision of a cleaner, safer, body-positive world.”
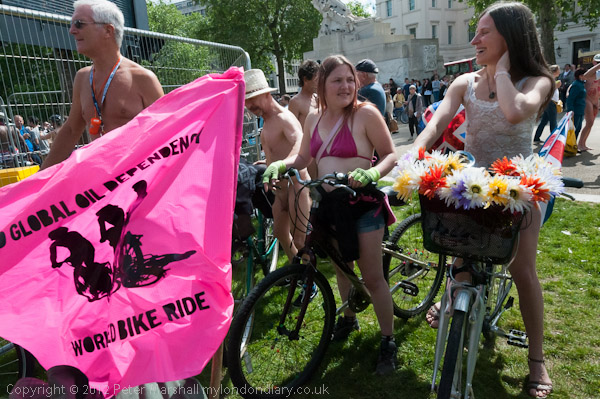
Back in 2012 there were similar rides in 20 countries around the world ands well as others in Brighton, Bristol, Cardiff, Exeter, Glasgow, Manchester, Portsmouth, Southampton and York.

After photographing the riders on the grass at Hyde Park corner I set off with them on foot, rather dangerously as other traffic was still driving around the busy roundabout and along Piccadilly. But I soon got out of breath and had to rest.

Later I took the tube to Westminster and met the cyclists again coming down Whitehall, going with them across Westminster Bridge. I left them to go to Waterloo Station on their way to the City and then back trough Holborn to Buckingham Palace and Hyde Park Corner.

Many more photographs at Naked Cyclists Ride Against Oil.
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.