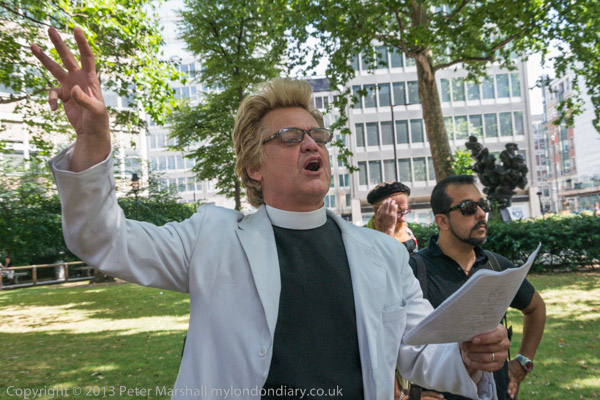
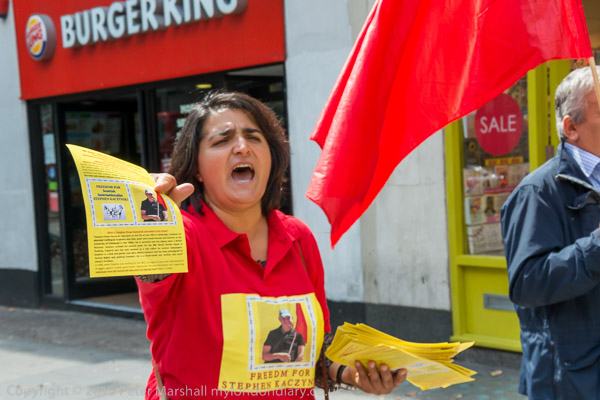
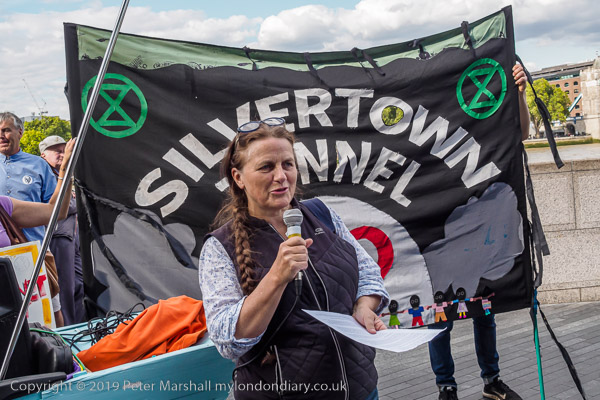
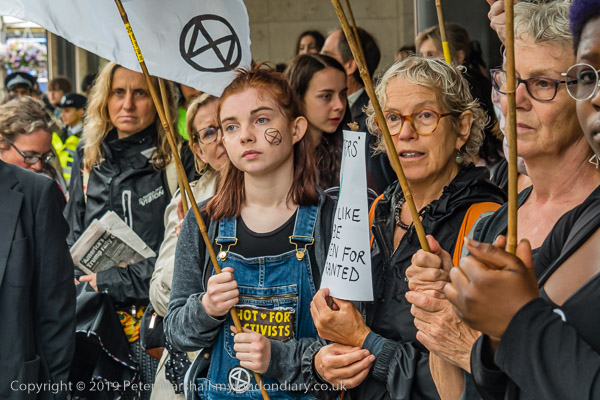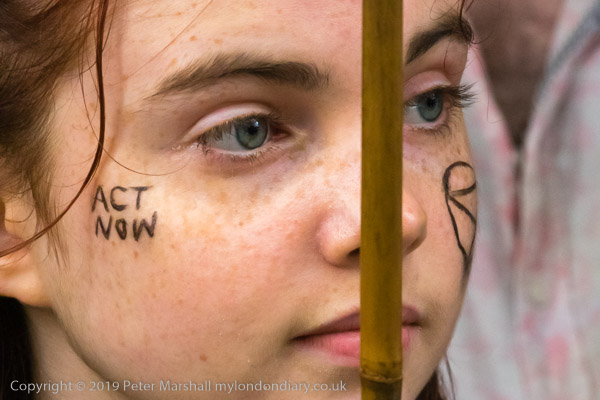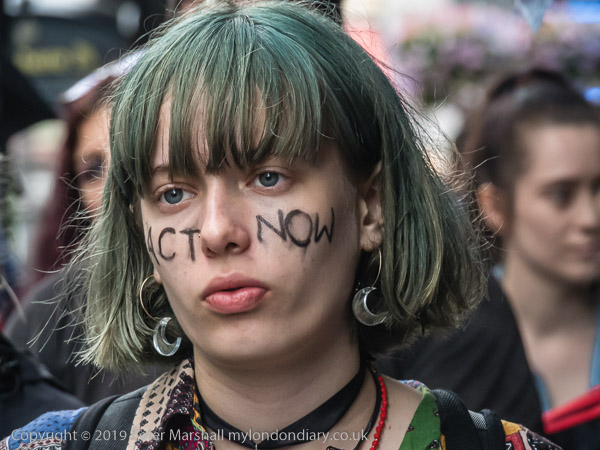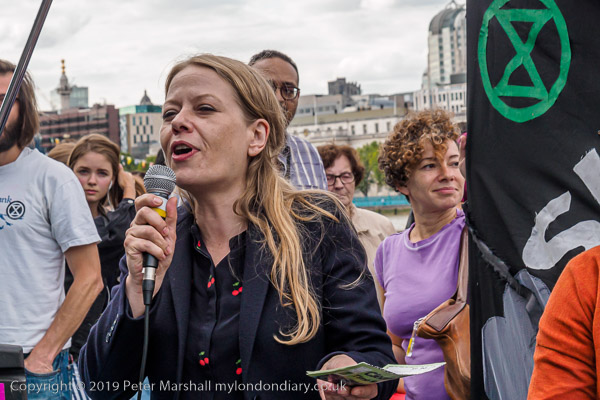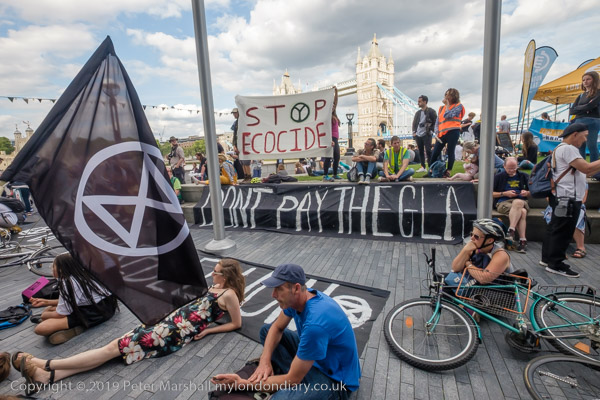Eight years ago on Saturday 27th July 2013 my working day began with the Rev Billy on a small green space on Victoria Street preparing the Stop Shopping Choir and volunteers for a “radicalized midsummer cloud forest dream” performance against the support given to fossil fuels and climate chaos by the banks and the City of London.
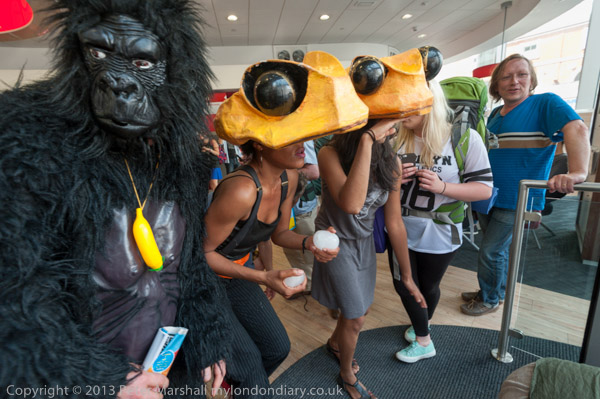
I’m not sure what staff and customers at the HSBC close to Victoria station made of the event, which pointed out that in the two previous years the top five UK banks raised £170 billion for fossil fuel companies, with HSBC in the lead. The Golden Toad costumes were for the Central American species forced into extinction by climate change in the 1980’s and recent weather events have now forced even the more sceptic to take the crisis seriously, even if so far to take little actual action.

After the performance in the bank, and as police began to arrive the group made their way to a wide area of pavement outside and staged another performance watched by pedestrians in the busy street close to the station, before leaving to celebrate in a nearby café.
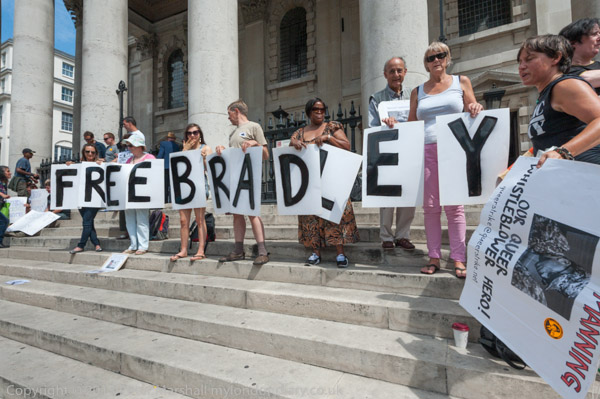
I left to go to Trafalgar Square where as a part of an international day of action the Bradley Manning Support Network held a vigil at St Martin-in-the-Fields. The ‘gay whistleblower’, now Chelsea Manning, was being celebrated in countries across the world for passing documents to WikiLeaks which exposed a great deal of illegal and immoral actions by the US and other governments and had recently been awarded the Sean MacBride Peace Prize and was then on trail in Fort Meade. She was later sentenced to 35 years in a maximum security jail, but this was commuted to around seven years by President Obama and she was released in 2017.

From there I made my way to the US Embassy, then still in Grosvenor Square, for a rally before the start of march organised by BARAC against Global Racism and Injustice in solidarity with families of Trayvon Martin, Stephen Lawrence, Azelle Rodney, Jimmy Mubenga and many others, aimed a highlighting the reality of racism and demanding justice, both in the UK and US.
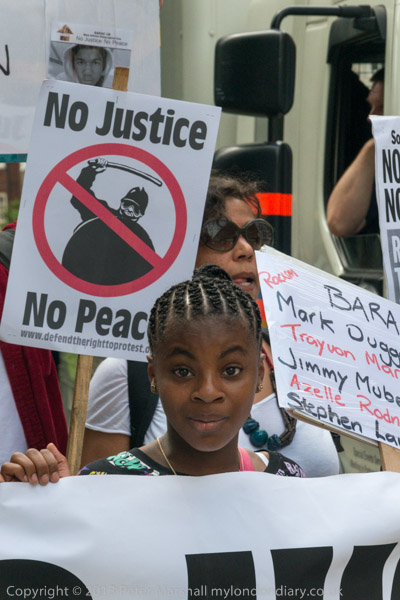

Although the march had been prompted by the acquittal in Florida of the murderer of Trayvon Martin which had led to a global outcry, the emphasis of the speeches at the Embassy was very much on events here in the UK. In his speech Lee Jasper of BARAC after mentioning the Martin case went on to say:
“We march to support the call from the Lawrence family for a full and independent judicial led public inquiry into the allegations that the Metropolitan Police sought to smear both the family and supporters through a covert police surveillance unit.”
“We march for Jimmy Mubenga, Mark Duggan, Kingsley Burrell, Smiley Culture and Azelle Rodney. We march for justice and equality in the 50th anniversary year of Dr Martin Luther King’s 1968 March on Washington. The truth is that his dream is a threadbare vision here in the UK where racism is on the rise amplified by austerity.”
My London Diary

After an hour or so of speeches the marchers left to march to a further rally at Downing St, but I left them as they went down Oxford St.
Against Global Racism and Injustice
Free Bradley Manning Vigil
Rev Billy at HSBC
All photographs on this and my other sites, unless otherwise stated, are taken by and copyright of Peter Marshall, and are available for reproduction or can be bought as prints.