DPAC – Stop & Scrap Universal Credit: A couple of days ago the media were carrying news of a report by the Resolution Foundation on the working of the Universal Credit benefit first introduced in 2013. This found that seven in 10 (71%) families on UC were worse off in real terms now than they would have been under the previous benefits, and that out of work people with disabilities were those likely to have lost most.
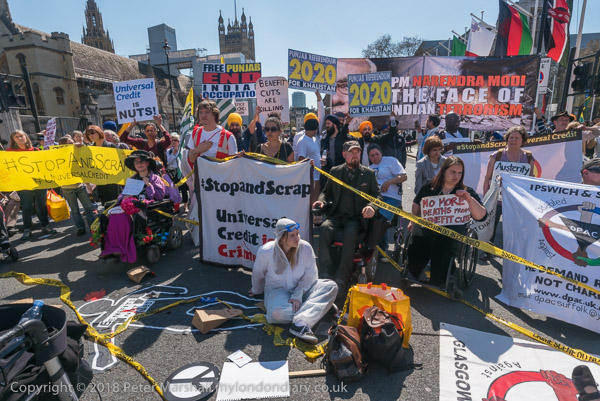

Six years ago, DPAC were already pointing this out and on Wednesday 18th April 2018 campaigners from DPAC (Disabled People Against Cuts), MHRN (Mental Health Resistance Network), Black Triangle, Winvisible and others began a nationwide day of action against Universal Credit in London with a rally in Old Palace Yard and a protest inside Parliament.
Security meant I was unable to cover their protest inside the Houses of Parliament but I met those who had been protesting inside when they came out to join those protesting outside and held a rally in Old Palace Yard.

As that rally ended the campaigners marched into Parliament Square where they blocked the roadway for around half an hour before ending their protest.

DPAC and others say that Universal Credit has so many flaws it must be scrapped, calling it “an economic and political disaster bringing further distress and impoverishment to those forced to endure it“.

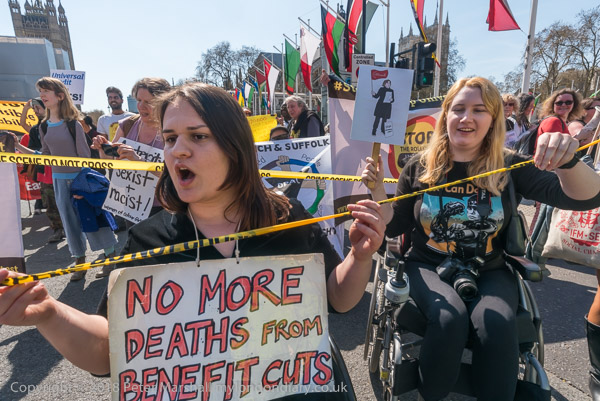
Back in 2018 they pointed out it has been particularly disastrous for disabled people. The removal of Severe and Enhanced Disability Premiums means single disabled people lose around £2,000 per year and a disabled couple over £4,000.
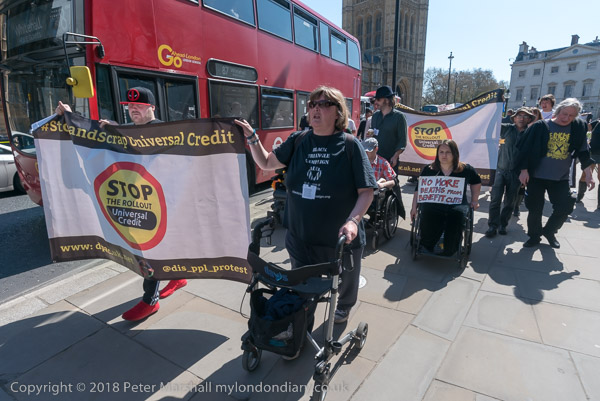

There have been some changes in Universal Credit since 2018, but these have mainly been administrative and have not affected the basic unfairness towards the disabled. The Resolution Foundation report suggests that a single person with a long-term disability which prevents them from working would now be £2,800 per year worse off than under the old benefits system.

Their report suggests overall cost of Universal Credit in 2028 will be about £86bn a year, while under the previous system it would have been £100bn, a saving of £14bn, which is being made to the cost of those disabled and others out of work – the poorest groups in our society. In contrast those working and also claiming UC will be a little better off than under to previous benefits system.
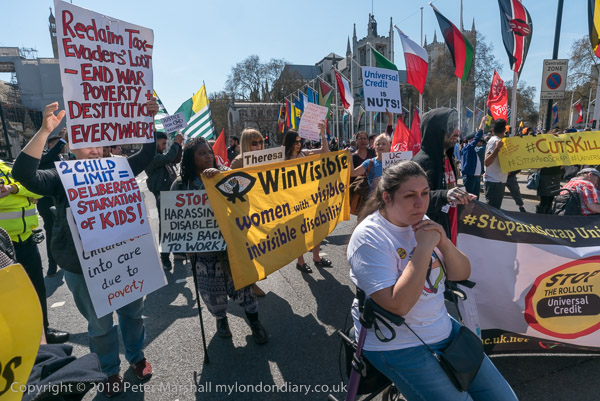

As always police found dealing with disabled protesters difficult. It doesn’t look good to be harassing them in the way they would normally act to protesters, and they have a great problem in making arrests of people in wheel chairs or on mobility vehicles. Apparently the Met have only one vehicle which can safely carry either – and only in limited numbers, perahps one at a time.
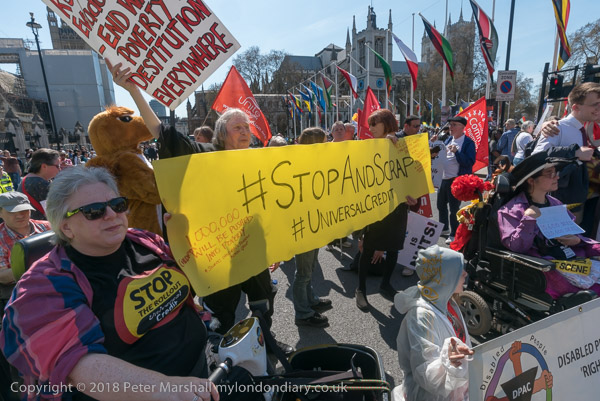

More about the protet and more pictures on My London Diary at Stop & Scrap Universal Credit say DPAC.
As well as this protest there was also a large protest in Parliament Square by Kashmiris and Indians from many sections of the community including Tamils, Sikhs, Ravidass, Dalits, Muslims and others against the visit by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, and smaller groups supporting him and his ultra-right Hindu supremacist policies.
Indians protest President Modi’s visit
Hindus support Modi
Save Girl, Educate Girl
And in late afternoon I went to join Environmental group Biofuelwatch holding their ‘Time to Twig’ Masked Ball Forest Flashmob outside the Marylebone hotel where the largest international biomass conference was taking place.
‘Time to Twig’ Masked Ball
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.



































