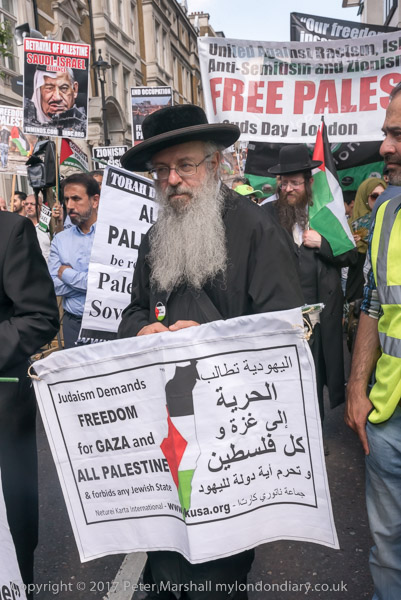
Disabled Lose Independence & Robin Hood Gardens Doomed: The Independent Living fund which enabled many disabled people to live useful and fulfilling lives ended on Tuesday 30th June 2015. After photographing the delivery of petitions ouside Downing St against its ending I went to Poplar for another visit to Robin Hood Gardens where a second attempt to get these important buildings listed had recently been rejected.
DPAC’s ILF Closing Ceremony – Downing St to Old Palace Yard
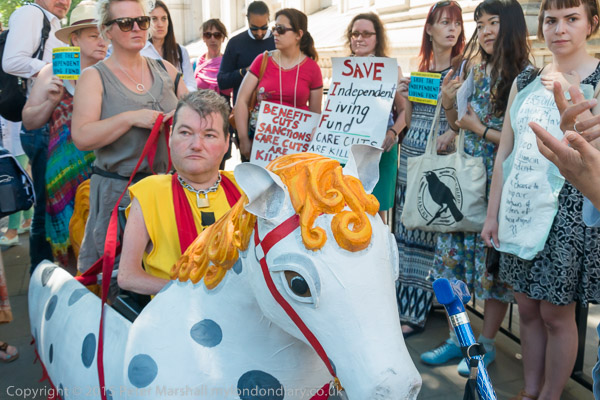

On the day the Independent Living Fund closed, campaigners for independent living for disabled people led by DPAC, Disabled People Against Cuts, presented petitions to the Prime Minister before marching behind the Threepenny Opera horse to Parliament to continue their fight for dignity and equality.
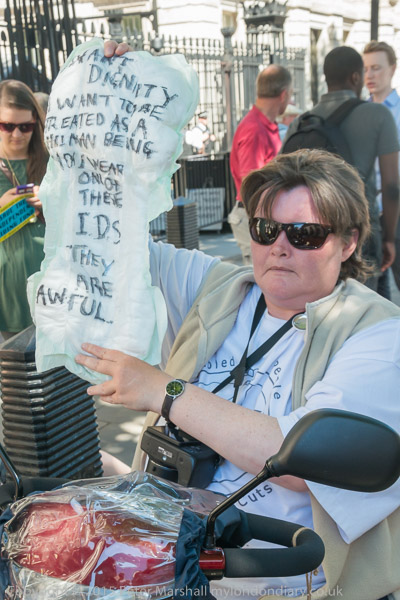
At the gates of Downing Street protesters wrote slogans on incontinence pads which losing the support means some will be forced to use. Paula Peters had this message for Iain Duncan Smith: ‘I want dignity – I want to be treated as a human – You wear one of these I. D. S. They are awful‘.’

As Secretary of State for Work and Pensions IDS was responsible for the decision to end this support, which had been introduced in 1988 to enable disabled people to live in their own homes and to pay for care, and in particular to employ personal assistants.
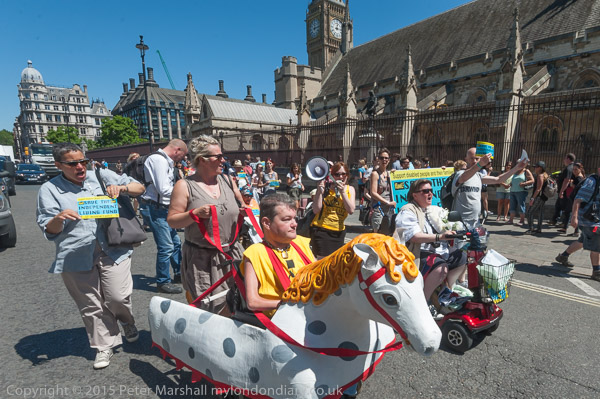
They had brought a petition with over 25,000 signatures to hand in and after this they marched to a rally at Old Palace Yard at the end of which a wreath with the message’s ‘RIP ILF’ was laid.

The government lost a legal challenge over ending the ILF but still closed it for new claimants on 1st July 2015. The responsibility for existing claimants in England was passed from the Independent Living Fund to local authorities who became responsible for care provision and all assessments. Support which had been well-administered became a post-code lottery.
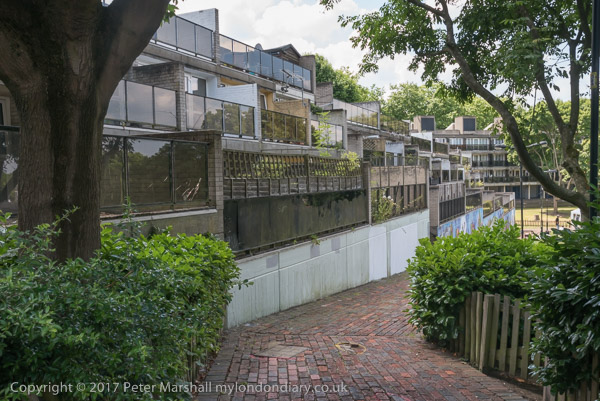
Robin Hood Gardens – Poplar
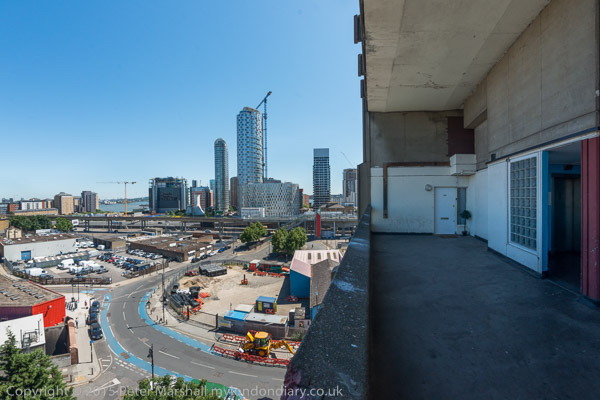

Robin Hood Gardens, designed by Alison and Peter Smithson and completed in 1972 was a nationally important and internationally recognised work of Brutalist architecture. Built for the London County Council with 213 flats, it was designed as two slab blocks, the east 10 storeys and the west 7 storeys on a difficult site next to one of London’s busiest roads – the Blackwall Tunnel Approach – but with a large and peaceful green inside.

It was very solidly built and the flats were generous, with wide ‘streets in the sky’ outside. Inside the flats next to the roadway you could hardly hear the traffic.
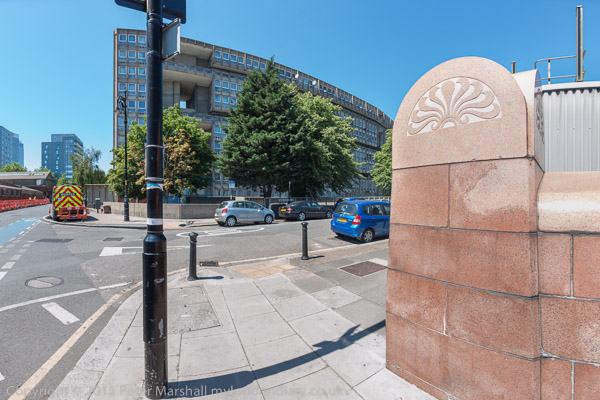

In 1965 ownership passed to Tower Hamlets Council who neglected the site, allowed the green to become overgrown and later actively demonised the estate and housed many problem families there.

Following a visit there in 2009 on an Open House Day tour led by Bridget Cherry I commented it was “in many respects a fine solution to a difficult site with some superb landscaping in the large interior space. Deliberately encouraged to ruin by overcrowding and use as a sink estate by Tower Hamlets, it is now in a sorry state, but the decision not to list it is unfathomable (or perhaps simply political.) I hope the campaign to save it from demolition succeeds. “
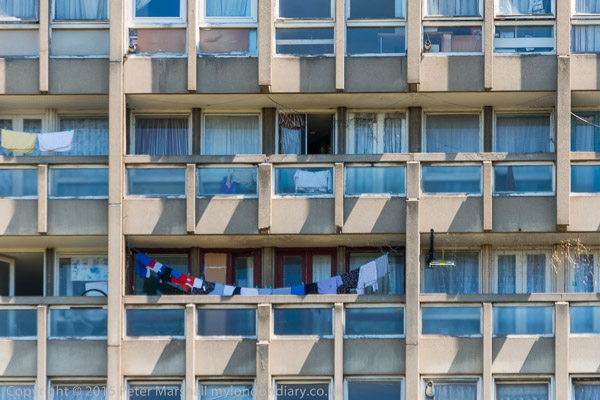

Most of the flats in the East block were then still occupied. They are large and desirable properties, but often have been used to house difficult residents.
During the New Labour government the listing advisory committee of English Heritage wanted to list it, but were overruled by the politicians, with then Minister of Culture Andy Burnham issuing a certificate of immunity in 2009 and allowing the local Labour Tower Hamlets council to proceed with plans for demolition and redevelopment of the area. But for the moment it was saved by the financial difficulties.
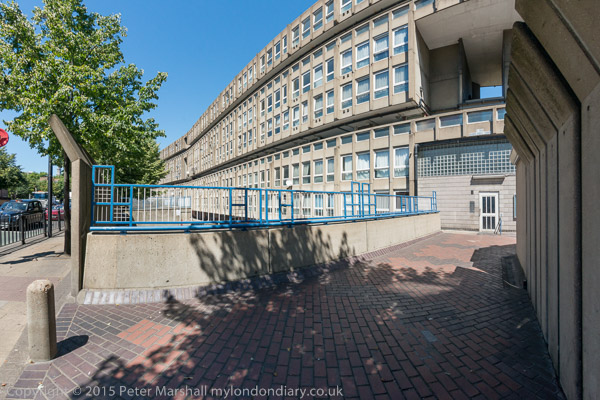

The immunity expired in 2014 and a further attempt, backed by almost every well-known British architect, was then made to get it listed, but was rejected by Historic England, the body that now control listings.
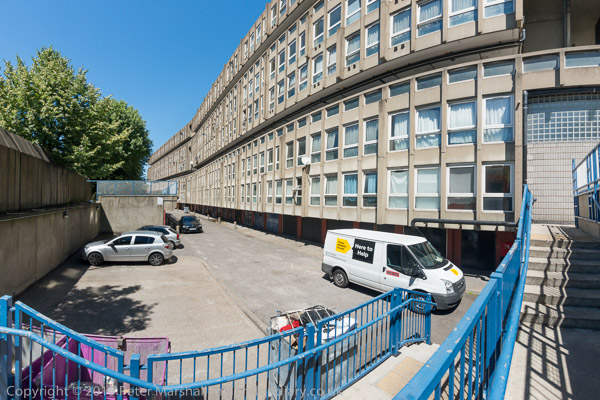

Parking areas on the outside of each of the two blocks
An open letter signed by Richard Rogers and others stated:
"The buildings, which offer generously sized flats that could be refurbished, are of outstanding architectural quality and significant historic interest, and public appreciation and understanding of the value of Modernist architecture has grown over the past five years, making the case for listing stronger than ever."Historic England went along with the local council’s views and judged that it “fails as a place for human beings to live“. This wasn’t the impression I got from talking to residents on my visits.
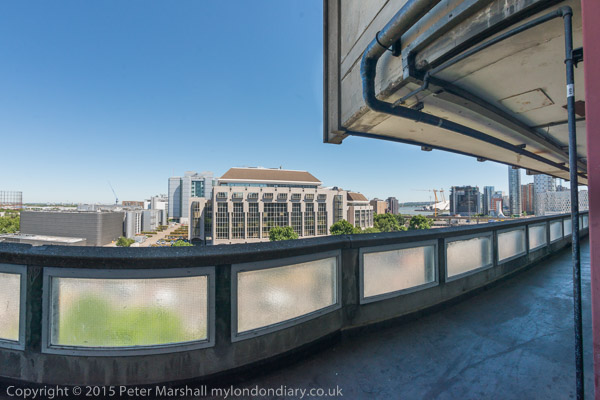

The defects of this and other soundly built modern estates that have been demolished – such as the Heygate at Elephant & Castle in Southwark can generally be easily and relatively cheaply overcome by refurbishment – improved door security, lift maintenance, window replacement, non-combustible cladding etc. The true reasons for demolition are financial, driven by the profits of the developers and also the financial problems of local authorities.

Demolition of sound buildings like this with the expectation of many years of useful service should be criminal. It represents a huge wastage of resources and an incredible carbon footprint both in the actual demolition and also for the rebuilding. The west block was demolished in 2017-8. The east block took around nine months to demolish and this was only completed in March 2025.
More at Robin Hood Gardens.
Flickr – Facebook – My London Diary – Hull Photos – Lea Valley – Paris
London’s Industrial Heritage – London Photos
All photographs on this page are copyright © Peter Marshall.
Contact me to buy prints or licence to reproduce.
















