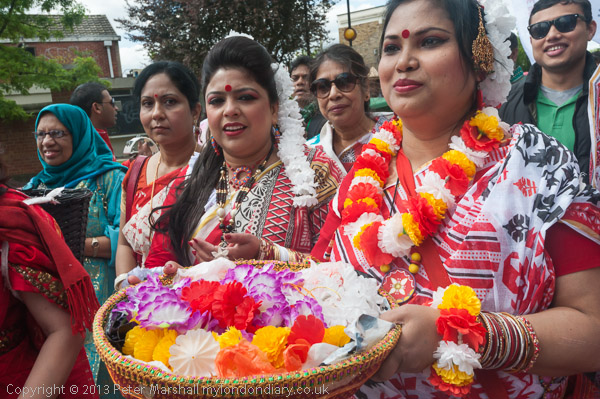Gun & Knife Crime, Equiano & St John’s: I went to two events in North London on Sunday 14th October 2007, a local march against gun and knife crime and then a Black History Month event in Abney Park Cemetery. And on my way home I stopped to take a few pictures of the church opposite Waterloo Station.
Communities Against Gun and Knife Crime, Hackney
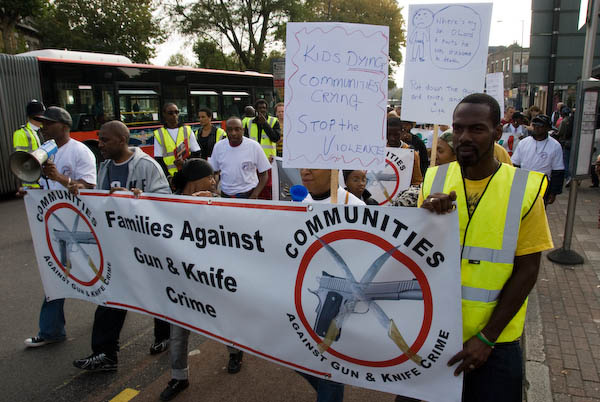

In the 2000’s a stretch of road between Upper Clapton and Lower Clapton attracted the title ‘Murder Mile’ in the press after eight people were shot dead on the street or in the streets just off the main road over a period of two years. Of course there are some other cities around the world – including in the USA – where that number of deaths in a week or even a day would not be unusual. But London is generally a very safe city and Clapton is one of a number of areas which has more than its share of gun and knife crime.

This is an area with a number of night clubs and where drug dealing is common and a large proportion of the shootings and deaths are related to these, often involving people from outside the area.
But young people who live in and around the area are also caught up in gun and knife crime and one death is one too many, particularly when it involves your friends or family. Like many areas of London it houses a wide social mix, and these crimes particularly involve the poorer members of the community, many of whom are black.
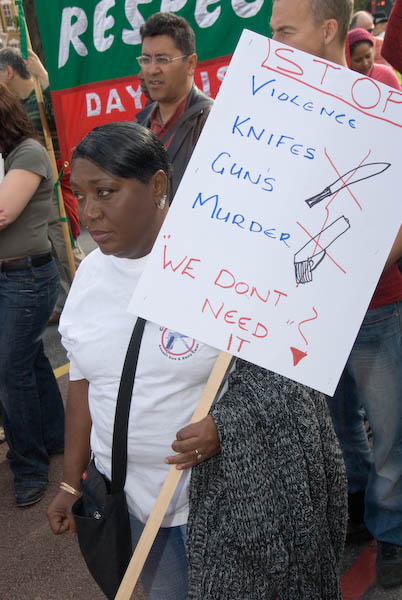

The march organised by Communities Against Gun And Knife Crime appeared to have no support from either of the two London Boroughs concerned – Hackney and Haringey – or from the Met police, who did escort it. The only other organisation which I could see was supporting it was Hackney Respect, a local group of the left-wing Respect party.
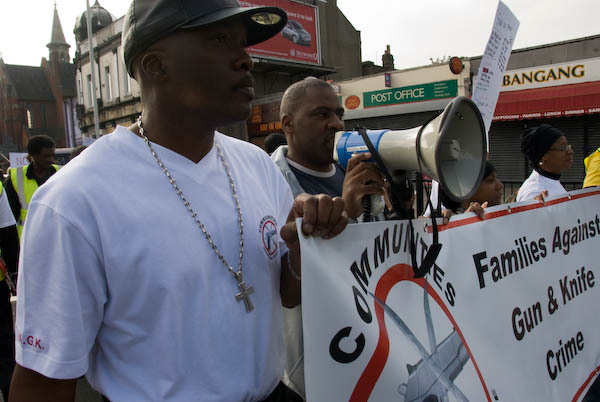
The march began at Clapton Pond with a prayer by a Black Church Sister, and then moved slowly north up the Lower Clapton Road and across the Lea Bridge Roundabout and up the Upper Clapton Road. I had to leave before the end for my second event.
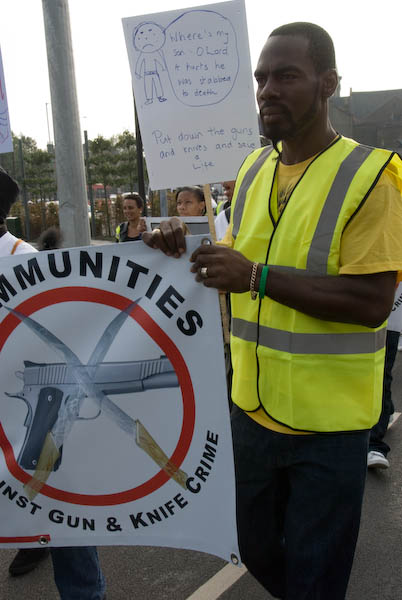

The march was smaller than I had expected with fewer than a hundred people taking part, and although it atrracted waves and shouts of support from people as it passed, few if any of them came to join it. As I commented, “marches like this are surely useful in raising community awareness, and it is hard to see why there was so little support from either the public, local authorities or other local groups – including the other political parties, churches and other community groups.” Apart from myself there was a photographer from a local paper reporting on the event, but no other media interest. I don’t think any of the pictures or my report which I filed to an agency were ever used.
Here is my final comment from my 2007 article:
The real challenge in cutting youth crime – and gun and knife crime is mainly youth crime – is getting people, and especially young people – real jobs that offer training and possibilities for advancement. At the moment there are too few jobs for young people, and many pay below a living wage, especially a living wage for London. While crime offers the only way to money, prestige and apparent success, many will take that route.
Communities Against Gun and Knife Crime
Equiano Society – His Daughter’s Grave – Abney Park Cemetery, Stoke Newington
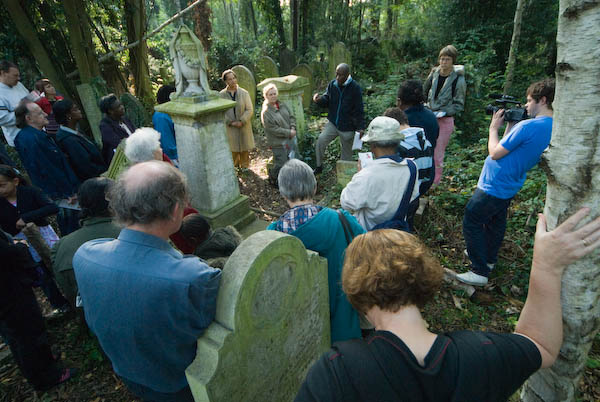

I joined a Black History Month walk led by Arthur Torrington OBE, the secretary of the Equiano Society which ended around the grave of Joanna Vassa, the daughter of Olaudah Equiano.

As the web site Olaudah Equiano, or, Gustavus Vassa, the African shows he was a truly remarkable man. Probably born around 1745 in what is now Nigeria he was kidnapped and sold into slavery as a child and taken to Barbados. In 1745 he became slave to a captain in the Royal Navy who renamed him Gustavus Vassa, and taught him to be a seaman and also sent him to school in London to learn to read and write. Later was bought by a Quaker merchant in Philadelphia who set him to work on one of his trading ships. Equiano was also able to engage in some trading for himself, and in four years made the £40 that his master had paid for him and was able to buy his freedom.
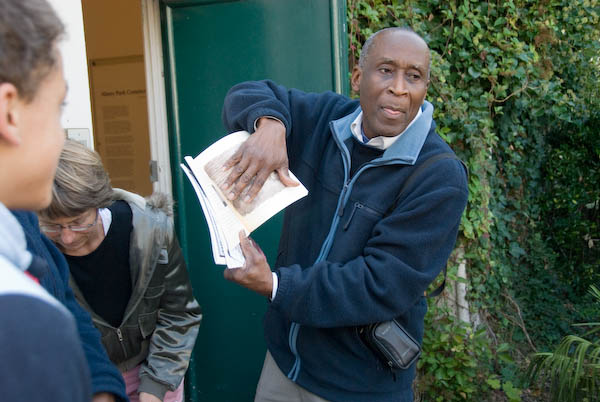

After various adventures in 1743 he came to London and became involved in the fight against slavery, although at first he was engaged in projects to set up black colonies in Central America and Sierra Leone, becoming for the latter the first black civil servant – but after he pointed out corruption among some officials he was quickly sacked.
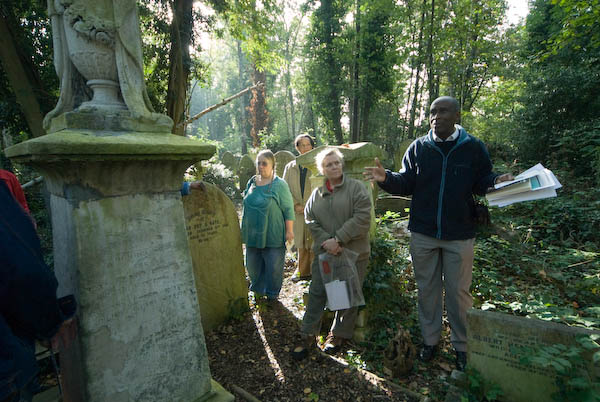

He then wrote the book which made him famous, ‘The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano, or, Gustavus Vassa, the African‘ which was an autobiography, a description of the horrors of slavery and a polemic calling for its abolition. It was a success when published in 1789 and he earned a considerable income from it. In 1792 he married an English woman, Susanna Cullen, at Soham in Cambridgeshire and they had two daughters, one of whom after his death in 1797 inherited his estate of £950 (equivalent to around £100,000 now.)
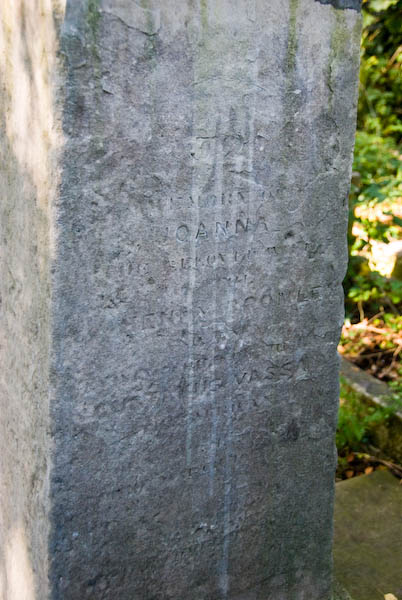

Joanna Vassa later married the Congregational minister, Henry Bromley, and in 2005 their joint grave (also of Henry’s second wife) was discovered in Abney Park Cemetery, fallen down and covered by moss and undergrowth. Much of the inscription was worn away, but the names remained and the stone was restored and re-erected.
St John’s, Waterloo – A Waterloo Church
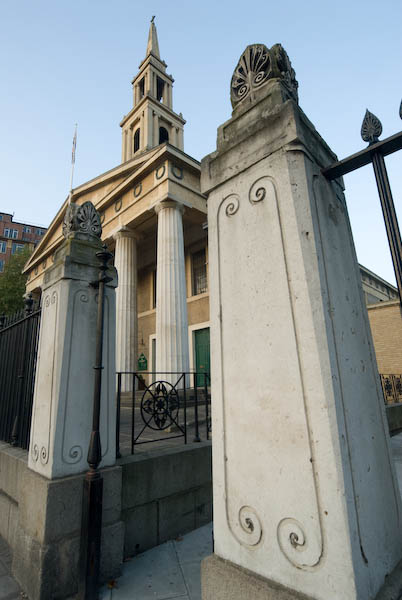

St John’s Church, now opposite Waterloo Station was one of a number of churches built in the years of national triumph following the defeat of Napoleon in 1815 with money granted by acts of Parliament to the Church Building Commission in 1818 and 1824 totalling £1.5 million. A total of 612 new churches were built by the Church Commissioners, mainly in the new and expanding industrial towns and cities, but initially “particularly in the Metropolis and its Vicinity“.
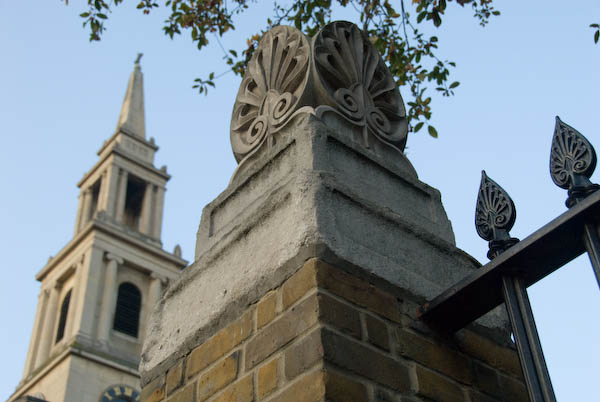

London south of the river was expanding rapidly, with new industries and a great deal of housing. The church was designed by Francis Octavius Bedford and built in 1822-1824 in a Greek Revival style – as were his other churches for the commissioners in Camberwell, West Norwood and Trinity Church Square, Southwark.

The site chosen, close to the foot of Waterloo Bridge was a difficult one, being a pond and a swamp, and John Rennie the Younger was consulted for advice about the foundations. This has proved sound as the building, despite being badly bombed in 1940 and standing in ruins until 1950 and the construction of the Jubilee Line underneath is still sound. It was restored and rededicated in 1951 as a part of the Festival of Britain, and again controversially in recent years which removed some of the later features.

I think I probably had just missed a train home from Waterloo Station opposite, a later development which opened as Waterloo Bridge Station in 1848, and had some time to wait for the next. Soon I was on a train home.