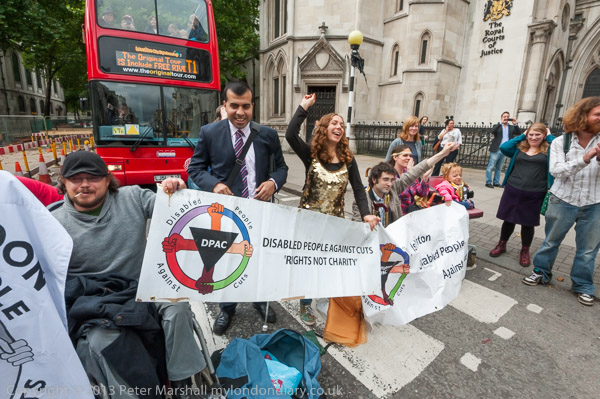Save Legal Aid – 2013: On Tuesday 30th July 2013, ten years ago today, the Save Legal Aid Campaign held a rally outside the Old Bailey in protest against proposed cuts in legal aid which they say would severely damage the UK justice system, removing legal aid completely for many and providing a poor quality cut-price service for others.

The proposals would bring in compulsory tendering on price, with legal aid services being provided by the lowest bidder and remove any choice by defendants of who should represent them. They say this would replace all the current specialist solicitors by groups such as Tesco and Eddie Stobart employing less qualified and experienced people and providing an inferior service for those unable to pay – and so choose – their solicitors.

The rally also celebrated the successes of the UK’s legal aid system, which speakers said had been the envy of the world since it was brought in on 30th July 1949, exactly 64 years earlier, an event celebrated with the singing of ‘Happy Birthday’ and the cutting of a cake by MP Diane Abbott.
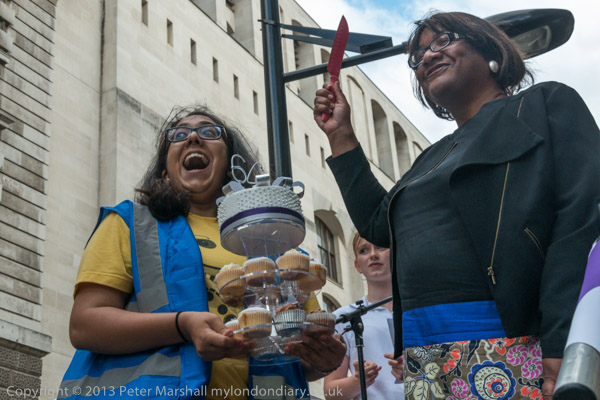
For many of us those celebrations rang hollow. The legal aid system by 2013 was but a pale shadow of that brought in by the Legal Aid and Assistance Act on 30th July 1949. It was a skeleton that was being celebrated, although one that as several speakers who had benefited from it showed still had some effect. In the unlikely event we ever get a reforming Labour government it could perhaps still be revived, but more likely any future government will destroy it still more as New Labour did.
Legal cases in the UK are incredibly expensive in part because of the nature of our legal system which is an adversarial one, but also because of some traditional practices which render it less efficient and protect the interests of some of those who are a part of the system.

Probably the only sound legal advice is to stay away from the law unless you are very rich. Although its often said that the same law governs both rich and poor, in practice that is not really the case, and in particular those in the middle of society get screwed.

Legal Aid was first introduced in the UK in 1949 when the welfare state was attempting to make justice fair for all. It could be claimed for almost all criminal or civil matters except libel and defamation and around 80% of the UK population were eligible for some support, with those more able to pay receiving support on a sliding scale depending on their income.
It wasn’t then a great cost to the economy as then only a small fraction of the population gad access the the legal advice that might have led them to take action in the courts. If you were poor you seldom came to court except when arrested – and most cases were dealt with by magistrates with legal aid seldom being involved.

In the 1970s Law Centres were set up in many of the poorer areas of the country, giving free advice and explaining and aiding their clients to take matters of social welfare, housing and criminality to the courts. And in 1973 a ‘Green Form Scheme’ was set up to allow those of low incomes to get legal advice from solicitors. Both led to increases in cases and a corresponding increase in the overall cost of legal aid.

The Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1962, the Commonwealth Immigrants Act 1968, the The Immigration Act 1971 and the the British Nationality Act 1981 each led to a predictable and dramatic increase in the number of cases requiring legal aid to resolve disputes.
Various actions were taken to reduce the cost to the country of legal aid, with eligibility being drastically reduced both by income limits and by reducing the areas of work for which it was available.

New Labour reformed the system when they came to power, but their reforms proved a disaster and they piled a second disaster on top by privatising the system. By the time the coalition government came to power there wasn’t really a great deal left, but their Legal Aid, Sentencing and Punishment of Offenders Act 2012 (LASPO) saw off most of what remained.

Since then, to get legal aid you have to have a disposable income of less than £733 a month and less than £8000 of disposable capital. Those receiving universal credit and some other benefits also qualify. There are different income and asset qualification levels for criminal proceedings in Crown Court cases.
As well as these tests legal aid is only available if your case passes a “merits” test as defined by The Civil Legal Aid (Merits Criteria) Regulations 2013. It has to be assessed by the Director as being in the public interest and having at least a 50% chance of success.
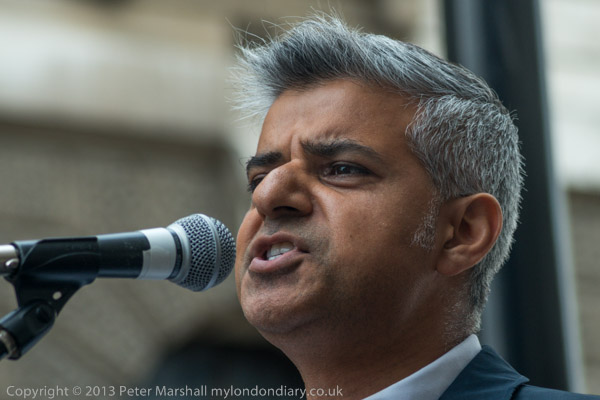
Speakers at the protest included Raphael Rowe, wrongly imprisoned as one of the M25 three, Anne Hall the mother of Daniel Roque Hall, a man suffering from a rare condition who would have died in prison without legal aid which got him released to receive care, and Sally, the mother of a rape victim who police failed, as well as Sadiq Khan MP Labour’s Shadow Justice Secretary, Ian Lawrence of NAPO, activist, poet, co-founder and co-chair of BARAC Zita Holbourne, Shauneen Lambe of Just for Kids Law and criminal defence solicitor and Justice Alliance member Matt Foot, but the loudest applause was for a rousing speech by Shami Chakrabarti of Liberty. You can see pictures of all of them and more about the protest on My London at Save Legal Aid.