On 6th August 1945 a US B-29 bomber dropped a atomic bomb, code name ‘Little Boy’, from a height of 31,000 ft over the Japanese city of Hiroshima. It took almost 45 seconds to fall to a height of 1,900 feet where it detonated, by which time the bomber, Enola Gay was over 11 miles away.

Hiroshima was a large city, a port with many industrial and military sites and a population of around 350,000. Because it had been selected as a target for a nuclear bomb it had not suffered the intensive conventional bombing of most other Japanese cities. The USA wanted to be able to see clearly the damage an atomic weapon could cause.

Around 70,0000 people, 30% of the population were killed by the initial blast and firestorm which was caused, with around the same number badly injured. Around 70% of the city’s buildings were destroyed, an area of almost 5 square miles devastated. Those killed included over 90% of doctors and medical staff who were concentrated in the central area of the city.
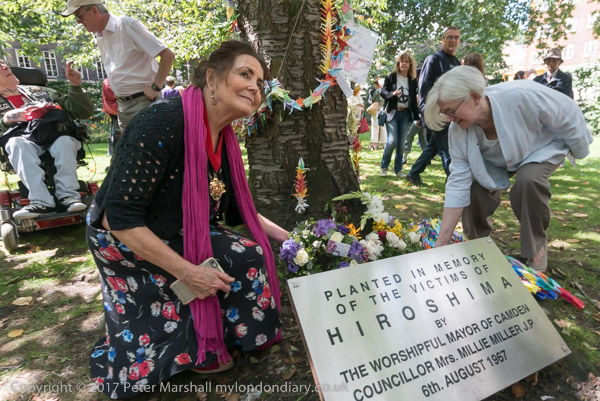

Two days later on August 8th the US decided to drop the second atomic bomb, one of a different design using plutonium rather than uranium, code-named ‘Fat Boy’. The intended target was Kokura, an ancient Japanese city with a huge arsenal, but dark clouds obscured the city, and the B-29 ‘Bockscar’ diverted to the city which was the secondary target, Nagasaki.

The black clouds may have come from the the previous days US conventional fire-bombing of nearby Yahata, but workers at the steel works in Kokura had apparently decided to burn coal tar to try to make a smokescreen. Or it could just have been bad weather or some combination of all three than saved Kokura and condemned Nagasaki.

There were clouds over Nagasaki too, but a patch of clear sky allowed the bomb to be dropped. The plutonium bomb was almost one and a half times more powerful than that which devastated Hiroshima but it exploded over a valley which slightly contained its effects. At least 35-40,000 were killed immediately, almost all of them civilians, including many foreign workers. Unlike in Hiroshima there was no firestorm as the area it was dropped on was less intensively developed.

Although it was the US who dropped the bomb, the British government was deeply involved. Under the 1943 Quebec agreement between Roosevelt and Churchill which brought scientific development of atomic weapons by the two countries together, the consent of the UK was needed for these weapons to be used.

Of course deaths continued after the explosions. Acute radiation syndrome killed many who survived the initial attack, mostly within 20-30 days. Radiation induced cancer and leukemia takes longer to emerge, reaching a peak around 6-8 years later. Radiation also causes miscarriages and birth defects.

Around 650,000 people were recognised by the Japanese government as ‘hibakusah’, survivors affected by the bombs, and around 1% of these had illnesses attributed to their radiation exposure.

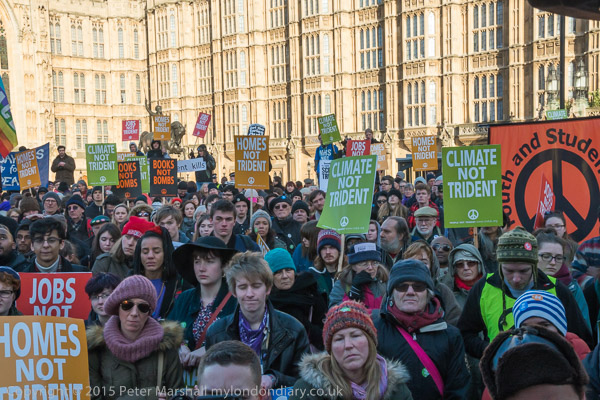
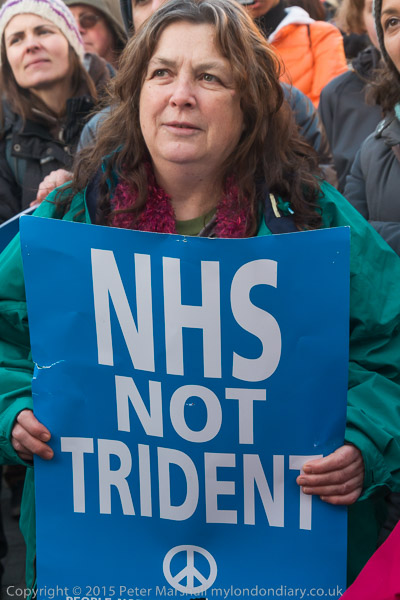
Ceremonies in the two cities and around the world remember the bombings and call for the outlawing of nuclear weapons, a total of around 13,000 of which are now held by China, North Korea, France, India, Israel, Pakistan, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States. The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons (TPNW) was adopted by the UN in 2017 and entered into force on 22 January 2021. Countries voting for its adoption included two former nuclear states, South Africa and Kazakhstan, who gave up their weapons voluntarily and North Korea. So far 55 states have ratified or acceded to the treaty.

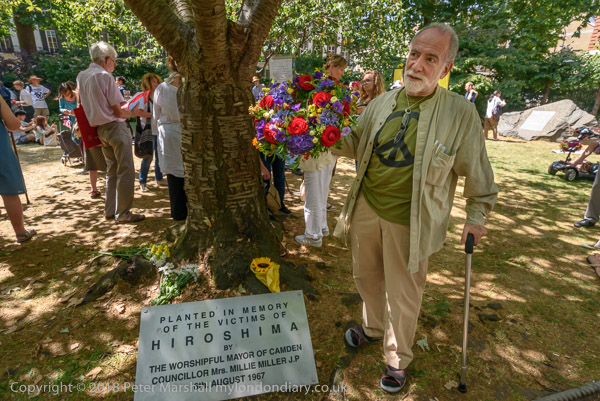
The pictures, taken in various years, come from the annual Hiroshima Day event held every 6th August in Tavistock Square in London organised by London CND. The square is in the London Borough of Camden and take place next to the Hiroshima cherry tree planted there in 1967 by the then Mayor of Camden.
All photographs on this and my other sites, unless otherwise stated, are taken by and copyright of Peter Marshall, and are available for reproduction or can be bought as prints.
All photographs on this and my other sites, unless otherwise stated, are taken by and copyright of Peter Marshall, and are available for reproduction or can be bought as prints.